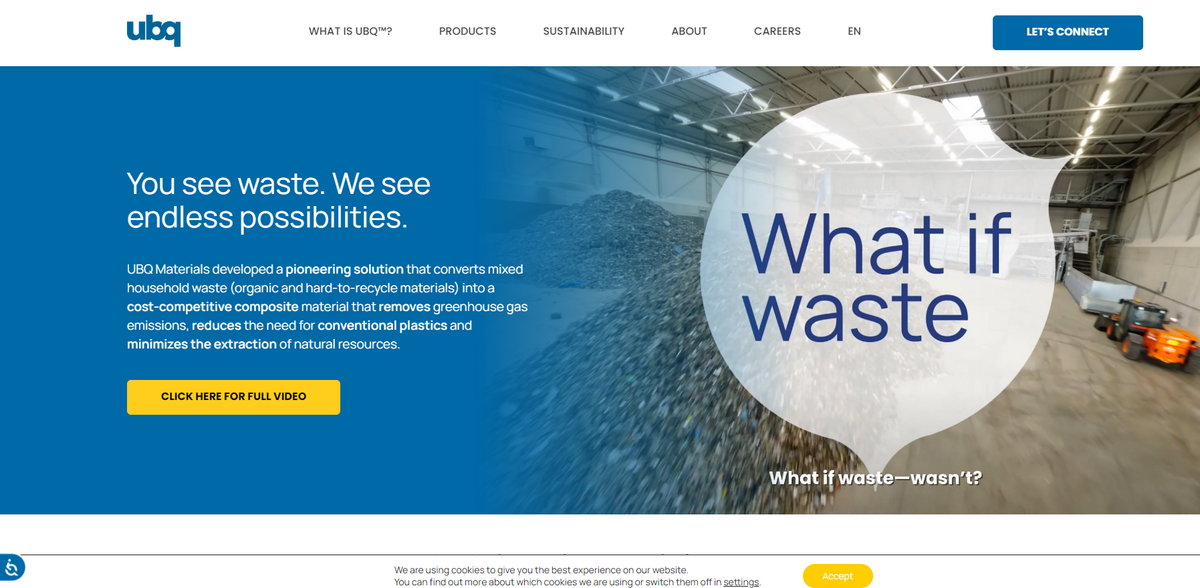
What the Project Is
UBQ™ is a climate-positive, thermoplastic composite, made from household waste, including all organics. This innovative material transforms unsorted household waste—including those hard-to-recycle plastics, trash, and garbage—into a bio-based thermoplastic composite that manufacturers can use directly in existing manufacturing processes. UBQ Materials developed a pioneering solution that converts mixed household waste into a competitive composite material, significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions and the need for conventional, oil-based resins. It simply gives new use to waste, preserving finite natural resources like fossil fuels, wood, minerals, and concrete.
Main Benefit
Key figures and facts on this advanced waste conversion technology include:
- Climate-positive material that prevents more greenhouse gases than it creates.
- 100% unsorted household waste is converted, including all organics and unrecyclable materials.
- UL 2809 Certified for containing 100% recycled content and fully recyclable at the end of its life.
- Cost-competitive pricing with no additional adaptation costs required by manufacturers.
- A USDA BioPreferred Certified Product containing at least 50% bio-based content.
Advanced Waste Conversion Insights
The project employs advanced waste conversion methods that turn everyday garbage into a consistently homogeneous, thermoplastic composite material. Manufacturers are finding it fascinating how this innovative process reduces waste by diverting it from landfills and incineration… and at the same time supports a circular economy. The technology bridges the gap between sustainable materials and renewable alternatives used in traditional plastic production.
Sustainable Production and Circular Economy
Integrating this technology into manufacturing processes allows for seamless replacement of conventional plastics with a sustainable alternative. By incorporating UBQ™, industries can effectively reduce the net carbon footprint of their end-products. The initiative emphasizes supporting the circular economy by recycling waste materials back into the production cycle while continuously targeting a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. This strategy is as much about preserving the environment as it is about innovating within the recycling industry.
Manufacturing and Implementation
Since UBQ™ is fully compatible with existing manufacturing processes, companies across various industries can implement it without costly modifications. This approach has led to significant use across segments where sustainable materials are in high demand. By leveraging unsorted household waste—including additives, secondary materials, and even polymers—the process not only creates a valuable composite but also marks a notable step towards reducing dependency on new natural resource extraction. It stands as a practical and competitive alternative to traditional oil-based resins.
Project Impact
- SDG 12 – Responsible Consumption and Production: Lowering waste by utilizing unsorted household trash.
- SDG 13 – Climate Action: Actively reducing greenhouse gas emissions and the environmental footprint.
- SDG 9 – Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure: Driving innovation in advanced waste conversion technology.
- SDG 11 – Sustainable Cities and Communities: Supporting sustainable development through circular practices.
Future Growth and Prospects
With a BCorp score of 108.8, this project marks a significant milestone in creating sustainable, economical alternatives to conventional plastics. It is not just about recycling or waste conversion; it is about converting trash into a resource and embracing a future where smart processing meets environmental responsibility. Manufacturers continue to explore the benefits of using UBQ™ to reduce costs, support renewable materials, and develop innovative end-products that drive sustainable growth. The momentum builds further as industries and municipalities see the value not only in adopting advanced waste conversion technology, but also in aligning with the growing global call for responsible production practices. It is a dynamic, engaging example of how technology—from converting everyday waste to any polymers into a valuable, bio-based material—can transform what many see as lacking potential into a cornerstone for future sustainable materials.