What the Whale Seeker Project Is
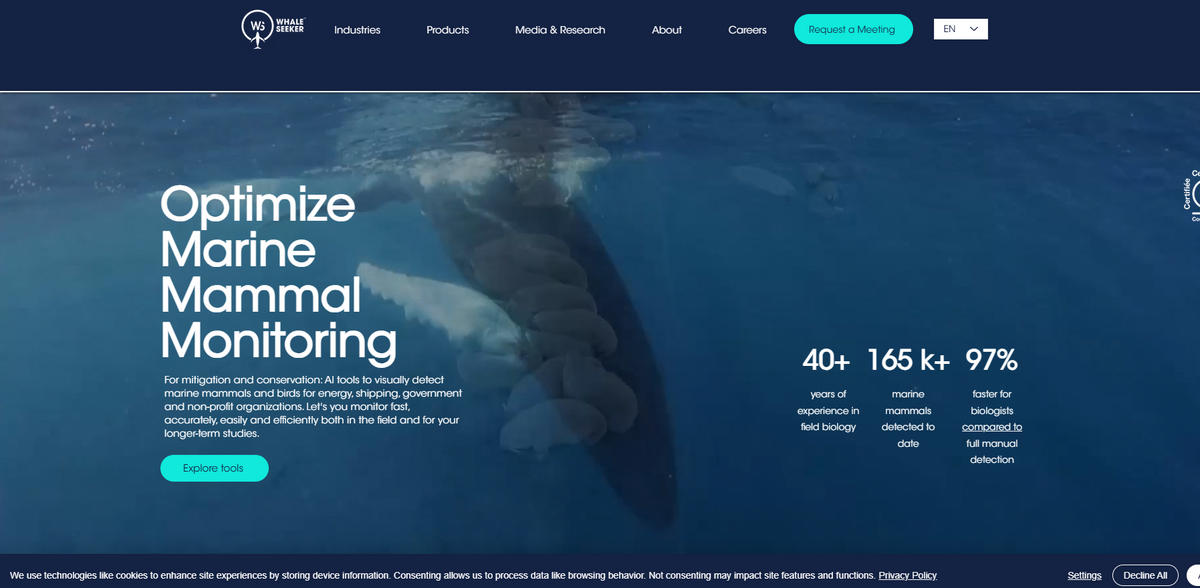
The Whale Seeker Project is an innovative initiative that leverages artificial intelligence and remote sensing technology to monitor marine mammals and birds, ensuring faster, more accurate, and efficient detection in various environmental contexts. With a refined focus on detecting species ranging from large whales to seals, this project supports conservation efforts, environmental management, and even pre- and post-project assessments for energy, shipping, government, and non-profit organizations. The project combines 40+ years of field biology experience with state-of-the-art AI tools, all to safeguard precious marine life while delivering data from aerial, satellite, infrared, and photo imagery. It has continuously evolved, often described as having an almost “wow” factor when its rapid detection speeds and contextual environmental insights come into play, making field studies and remote monitoring a seamless experience.
Main Benefits and Key Figures
The Whale Seeker Project offers numerous benefits, including streamlined detection processes, enhanced monitoring in remote areas, and the ability to capture vital data under a variety of environmental conditions. Its blend of human expertise with proprietary AI technology truly sets it apart by ensuring that marine mammal detection is not just advanced, but also ethical. Key figures include:
- 40+ years of experience in field biology
- 165K+ marine mammals detected to date
- 97% faster detection for biologists compared to full manual methods
Advanced Detection Technologies
The project stands out because of its diversified array of detection solutions. From the Möbius system, which combines aerial imagery with both human and machine judgments for enhanced reliability, to Möbius Observer that offers real-time alerts using drones – these tools are designed to work seamlessly in the field. Whats more, Cetus expands the project’s reach by analyzing imagery captured from space over vast areas, revealing migration corridors and pinpointing conservation hotspots. And then there’s Arc, which tackles the challenges of nighttime and adverse conditions using standard forward-facing cameras. All these components work together like a well-oiled machine, ensuring that monitoring is not only fast but also contextually aware.
Operational Flexibility in Monitoring
The Whale Seeker Project is recognized for its operational flexibility – a quality that enables monitoring wherever and whenever it is needed. Whether it is from shore, from a vessel, or through the use of drones, aircraft, or satellites, real-time marine mammal detection has never been easier. This flexibility facilitates project assessments in even the most remote or challenging locations, ensuring that permit requirements, conservation actions, and security measures are based on trustworthy insights. The approach is adaptable to varied contexts, whether the focus is on large cetaceans in the open ocean or on pinnipeds close to coastal areas.
Ethical Commitment and Transparency
A key differentiator of the Whale Seeker Project is its unwavering commitment to ethics and accountability. In an era where technology often raises concerns, the project champions a responsible approach to using AI for environmental conservation. By ensuring transparency and collaboration with governmental agencies, academic institutions, and maritime industry partners, it reinforces the importance of maintaining ethical practices in the deployment of AI in sensitive environmental contexts. This ethical framework underpins every aspect, allowing stakeholders to trust that the project not only delivers accurate data but does so with a clear moral compass.
Collaboration and Technological Integration
An impressive aspect of the Whale Seeker Project is its robust collaboration network. It brings together maritime industry partners, governments, and academic institutions to create a comprehensive monitoring ecosystem. Not only does this collaboration enrich the data collected – offering standardized insights for effective population comparisons – but it also supports long-term initiatives aimed at understanding the impact of climate change on marine migration and species health. The integration of advanced AI models with seasoned human expertise ensures that this data becomes actionable, supporting both conservation and environmental management strategies across diverse ecosystems, from polar regions to coastal areas.
Project Impact
- SDG 13: Climate Action – Informing strategies to mitigate climate change effects on marine ecosystems
- SDG 14: Life Below Water – Promoting the sustainable use and protection of the world’s oceans
- SDG 15: Life on Land – Contributing to the broader understanding of environmental interactions on coastal lands and ice
- SDG 17: Partnerships for the Goals – Fostering collaboration across governments, industries, and the scientific community
Future Outlook and Continued Innovation
Looking forward, the Whale Seeker Project continues to push the boundaries of what is possible in marine monitoring. With its cutting-edge AI technologies and operational versatility, the project is set to expand its detection capabilities – soon including nighttime operations and additional environmental variables. There is an unmistakable energy surrounding the vision to empower marine protected areas and promote safer, data-driven environmental decisions on a global scale. As the project evolves, additional advancements are expected to further reduce detection times while ensuring that crucial environmental data is captured with precision and care. It’s a dynamic journey that balances technological innovation with ethical considerations, making it an exemplary model for future environmental monitoring initiatives.