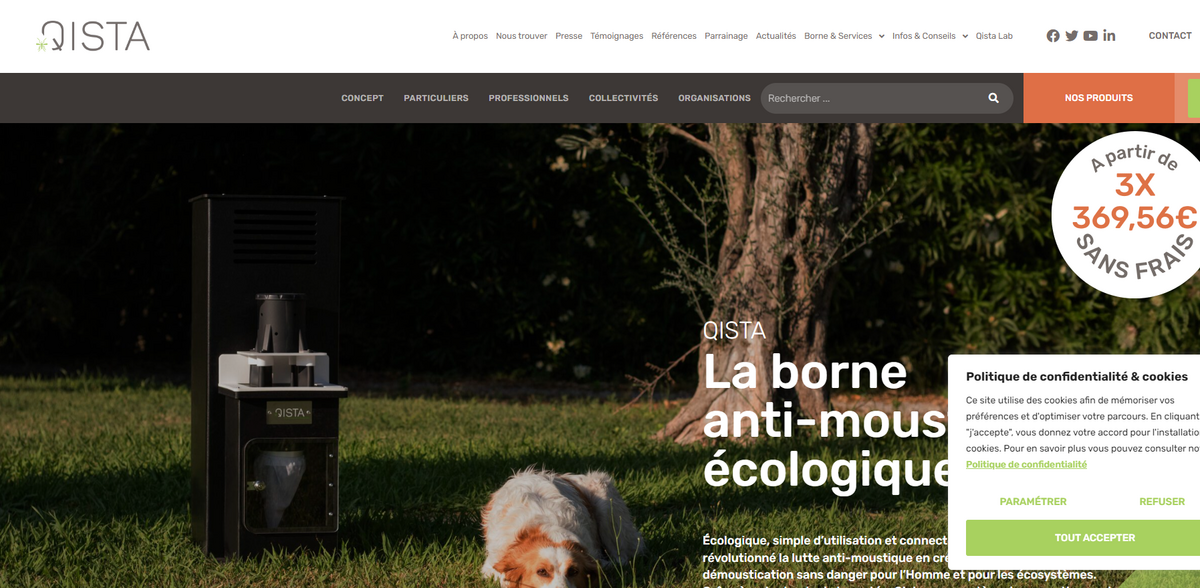
What is The Qista Project?
The Qista Project stands as an innovative and environmentally responsible solution that focuses on protecting victims of mosquitoes by eliminating the source of nuisance… It values outdoor spaces and reclaims them for outdoor living. At its core, the project is an ecological initiative born from the need to find a sustainable and preventive approach to mosquito control. The project combines science with environmental care by creating a connected anti-mosquito station, known as BAM, which is ecological, respects biodiversity, and especially avoids any insecticides. This pioneering method emerged as a strategic response to the catastrophic environmental impact imposed by large-scale chemical control methods, as revealed by scientific studies such as Dr. Poulin’s work at the Tour du Valat Research Center.
Main Benefits and Key Figures
The project delivers tangible and impressive outcomes that underline its effectiveness and commitment to sustainability. Key figures and notable achievements include:
- An 88% reduction in mosquito nuisance, as demonstrated during field trials.
- The initial installation of 16 anti-mosquito stations in the protected pilot village of Sambuc, located in a Natura 2000 area.
- Expansion to nearly 400 stations in Hyères alone, safeguarding public spaces and residents.
- International deployments extending to Europe, the South Pacific, and recently the United Arab Emirates with 720 new stations.
- A series of awards and recognitions, including honors at CES Las Vegas and integration into recognized eco-innovation incubators.
Origins and the Birth through Techno Bam
Born from the technical expertise of Techno Bam with support from the Tour du Valat Research Center and the Regional Natural Park of Camargue, this project emerged after scientists concluded that traditional chemical treatments were wreaking havoc on delicate ecosystems… Techno BAM’s realization about the environmental cost pushed the development of QISTA, a connected station that offers preventive protection without using chemical insecticides. This approach marked a turning point in ensuring a safe, biodiversity-respectful method of controlling the proliferation of mosquitoes – a classic case of innovation spurred by ecological necessity.
Project Evolution through Innovation
Since its inception in 2015, QISTA has constantly evolved. What started as a small-scale trial in a pilot village soon turned into an internationally recognized solution. Over the years, the project has seen major milestones: international installations across multiple continents, continuous research and development advancements, and vibrant participation at events such as COP 22 in Marrakech. The journey extended into newer phases when awards and accolades from bodies like World Efficiency, Med’Innovant, and Territoria recognized QISTA’s potential. The progression from a simple pilot project to an award-winning and widely deployed solution is a testament to the commitment embedded in its design and implementation… The recent introduction of the “BAM VISIO” encapsulates further improvements, cutting down energy consumption and recycled CO₂ use while reducing noise levels.
Protecting and Valuing Outdoor Spaces
Beyond the technical details and accolades, the project has always held a clear purpose: protecting and valuing outdoor spaces. With the development of QISTA stations for use by local authorities as well as private individuals, there is a renewed sense of reclaiming outdoor living areas. Municipalities across France and even abroad now equip public areas—urban landscapes, schools, daycare centers, nursing homes, and parks—with effective mosquito control systems. The idea is simple yet deeply impactful: allow communities to enjoy their outdoor spaces without the constant worry of rampant mosquito infestations.
Embracing Technological and Scientific Advancements
Technological innovation remains at the heart of QISTA’s progression. Over the years, the project has consistently integrated state-of-the-art features to improve performance and sustainability. By 2021, the launch of QISTA LAB marked a leap forward in entomological expertise with field studies conducted in locations like Djibouti—further tuning and refining the process. The continuous evolution of the anti-mosquito station, such as the introduction of the “BAM VISIO,” underscores the project’s commitment to manage resources better by consuming less recycled CO₂ and lowering energy use. This evolution reflects an ongoing investment into R&D efforts that not only preserve ecological balance but also push forward the boundaries of sustainable technology.
Project Impact on Sustainable Development Goals
- SDG 3: Good Health and Well-Being – By reducing mosquito-borne problems, the project directly supports healthier, safer communities.
- SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities – Enhanced outdoor spaces and public areas promote inclusive and sustainable urban living.
- SDG 13: Climate Action – The reduction of chemical treatments and optimized resource use contribute to a lower environmental footprint.
- SDG 15: Life on Land – By avoiding hazardous insecticides, the project preserves biodiversity and supports healthy ecosystems.
Looking Forward: Global Expansion
The future of QISTA is bright and decidedly international. With ongoing contracts such as the installation of 720 stations in the United Arab Emirates—making it the country most equipped with Qista technologies outside of France—the project is expanding its global footprint. Meanwhile, its role as a strategic partner for local authorities in vector control is solidifying further… These future-oriented steps are a reflection of the project’s capacity to adapt, innovate, and scale in the face of emerging global health challenges. The continuous focus on sustainable growth and international development underscores the project’s enduring commitment to creating safer, healthier communities while ensuring a minimal ecological footprint.