Understanding Sustainable Farming: A Pathway to a Greener Future
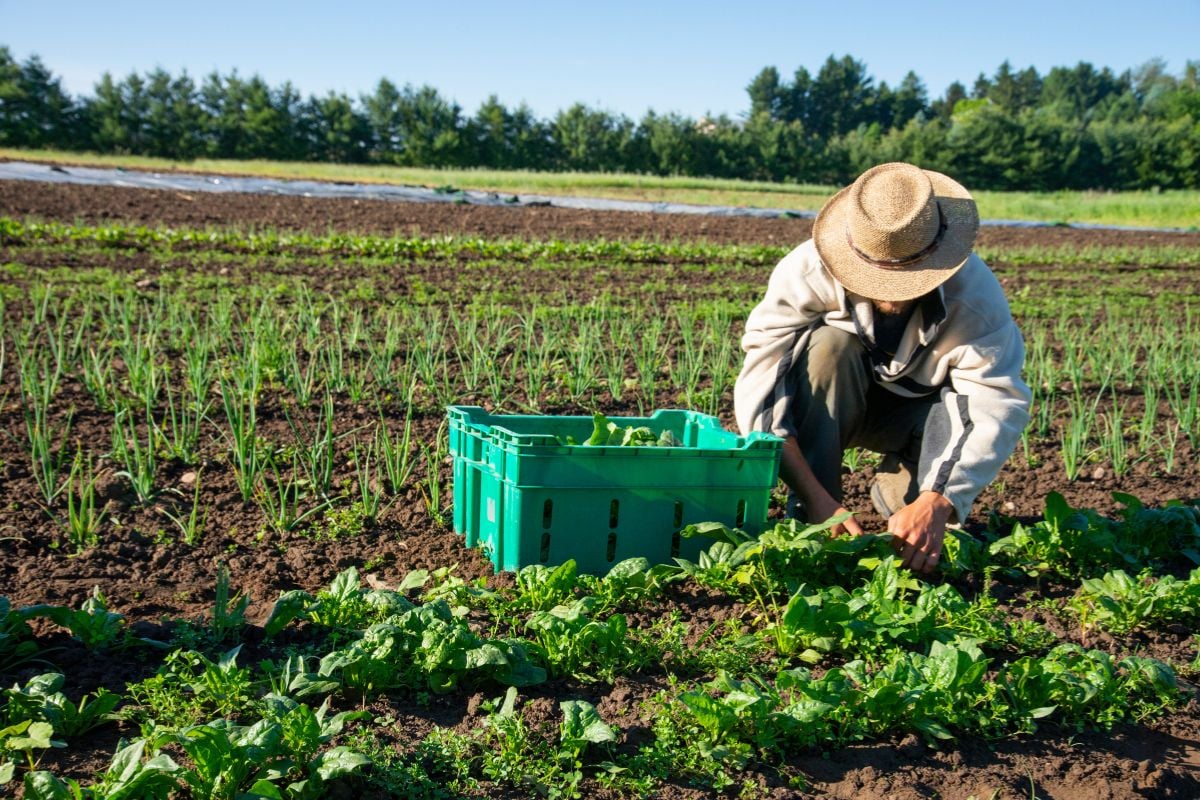
Sustainable farming is an agricultural approach that seeks to meet society’s food and textile needs in the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It integrates three main goals: environmental health, economic profitability, and social equity. Sustainable farming is not just a set of practices but a philosophy that aims to balance the needs of the environment, farmers, and consumers. This approach is crucial in addressing the challenges posed by climate change, resource depletion, and population growth. By adopting sustainable farming practices, we can ensure a healthier planet and a more resilient agricultural system.
The Principles of Sustainable Farming
Sustainable farming is built on several core principles that guide its practices. These include maintaining soil health, conserving water, reducing pollution, and promoting biodiversity. Soil health is maintained through practices like crop rotation, cover cropping, and reduced tillage, which help to prevent erosion and maintain soil fertility. Water conservation is achieved through efficient irrigation systems and rainwater harvesting. Pollution is minimized by reducing the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, and by managing waste effectively. Biodiversity is promoted by maintaining a variety of crops and livestock, which helps to create a balanced ecosystem and reduce the risk of disease and pest outbreaks.
Sustainable Farming and the Sustainable Development Goals
The United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) provide a framework for addressing global challenges, including those related to agriculture. Sustainable farming contributes to several SDGs, such as zero hunger, clean water and sanitation, climate action, and life on land. By promoting sustainable farming practices, we can help to achieve these goals and create a more sustainable and equitable world. For example, Lagarde Winery in Mendoza, Argentina, combines tradition with innovation to produce wines sustainably, contributing to the local economy and environment.
Examples of Sustainable Farming Practices
Many projects around the world are leading the way in sustainable farming. Penedo Borges in Mendoza showcases sustainable practices in wine tourism, while Dolium Winery revolutionizes sustainable winemaking by integrating traditional practices with modern innovations. In the realm of organic food, Las Quinas offers a range of certified organic products, emphasizing sustainability and health. Similarly, Capital Brewing Co in Australia blends sustainability with community support in their brewing process.
The Role of Technology in Sustainable Farming
Technology plays a crucial role in advancing sustainable farming practices. Precision agriculture, for example, uses GPS and remote sensing to monitor crop health and optimize resource use. This technology helps farmers to apply water, fertilizers, and pesticides more efficiently, reducing waste and environmental impact. Projects like BE WTR are revolutionizing water use by providing high-tech filtering systems that enhance tap water quality while minimizing environmental impact. Similarly, Mainstem Malt supports sustainable malt supply chains, promoting conservation and supporting local farmers.
Community and Economic Benefits of Sustainable Farming
Sustainable farming not only benefits the environment but also supports local communities and economies. By promoting local food systems, sustainable farming reduces the need for long-distance transportation, which lowers carbon emissions and supports local businesses. Projects like Nc’nean Distillery in Scotland use organic Scottish barley and renewable energy, setting a benchmark for sustainable whisky production. Similarly, Two Drifters Distillery produces carbon-negative rum, demonstrating a commitment to sustainability and community support.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its benefits, sustainable farming faces several challenges, including economic barriers, lack of awareness, and resistance to change. Many farmers are hesitant to adopt sustainable practices due to the perceived costs and risks. However, as awareness grows and technology advances, more farmers are recognizing the long-term benefits of sustainability. Initiatives like Drop Bear Beer Co. and JUBEL Beer are leading the way by demonstrating the economic viability of sustainable practices in the beverage industry.
Conclusion
Sustainable farming is essential for creating a resilient and equitable food system that can withstand the challenges of the future. By adopting sustainable practices, we can protect the environment, support local communities, and ensure food security for generations to come. Projects like Debuencafé and Brussels Beer Project exemplify the potential of sustainable farming to drive positive change. As we continue to innovate and collaborate, sustainable farming will play a crucial role in building a greener, more sustainable future.
Projects Overview
- Lagarde Winery: Sustainable winemaking blending tradition and innovation in Mendoza, Argentina.
- Penedo Borges: Gold-winning sustainable wine tourism with unique experiences in Mendoza.
- Dolium Bodega Subterranea: Revolutionizing sustainable winemaking with traditional practices in Mendoza.
- Las Quinas: Your organic food destination for sustainable delights.
- Capital Brewing: Sustainable brewing with community support for environmental impact.
- Frankie & Jet: Explore sustainability and flavor with organic herbal teas.
- ZYN: Turmeric-powered refreshments promoting health and sustainability.
- Sunwink: Sustainable wellness through plant power and community impact.
- Nc’nean Distillery: Leading sustainable whisky production with organic Scottish barley.
- Proud Source Water: Eco-friendly alkaline spring water in recyclable aluminum cans.
- Mainstem Malt: Sustainable malt supply chains supporting farmers and conservation.
- Two Drifters Distillery: Carbon negative rum with award-winning sustainability practices.
- BE WTR: Premium sustainable water solutions in reusable glass bottles.
- Charter Brands: Langley’s Gin blends traditional distilling with sustainability.
- Drop Bear Beer: Sustainable non-alcoholic brewing with carbon-neutral operations.
- Jubel Beer: Refreshing lager with a commitment to sustainability and community.
- Debuencafé: Compostable coffee capsules supporting sustainability and social impact.
- Brussels Beer Project: Innovative brewing with sustainability and community engagement.
- Steeped Coffee: Eco-friendly brewing revolution combining convenience and sustainability.
- Chimney Fire Coffee: Commitment to sustainability and ethical sourcing in coffee.
FAQ
What is sustainable farming?
Sustainable farming is an agricultural approach that aims to produce food while preserving the environment, supporting fair labor practices, and maintaining economic viability for farmers. It focuses on methods that are environmentally friendly, economically viable, and socially responsible.
How does sustainable farming benefit the environment?
Sustainable farming practices reduce pollution, conserve water, reduce soil erosion, and improve soil health. By using techniques like crop rotation, organic farming, and agroforestry, sustainable farming helps maintain biodiversity and reduce the carbon footprint of agricultural activities.
What are some common sustainable farming practices?
Common sustainable farming practices include crop rotation, cover cropping, reduced tillage, integrated pest management, and organic farming. These practices help improve soil health, reduce chemical use, and promote biodiversity.
How does sustainable farming support local communities?
Sustainable farming supports local communities by creating jobs, promoting fair labor practices, and encouraging local food systems. It helps build stronger economies by keeping food production and consumption within the community, reducing the need for long-distance transportation.
What role does technology play in sustainable farming?
Technology plays a crucial role in sustainable farming by improving efficiency and reducing waste. Innovations such as precision agriculture, drones, and data analytics help farmers optimize resource use, monitor crop health, and make informed decisions for sustainable practices.
How does sustainable farming align with the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals?
Sustainable farming aligns with several UN Sustainable Development Goals, including zero hunger, responsible consumption and production, and climate action. By promoting food security, sustainable resource use, and environmental protection, sustainable farming contributes to global efforts for a sustainable future.
What is the economic impact of sustainable farming?
Sustainable farming can lead to long-term economic benefits by reducing input costs, improving yield stability, and opening new markets for sustainably-produced goods. It fosters resilience against market fluctuations and environmental changes, ensuring economic viability for farmers.
Can sustainable farming practices be applied to large-scale agriculture?
Yes, sustainable farming practices can be adapted to large-scale agriculture by integrating technology and innovative practices. Techniques like precision agriculture and agroecological approaches can help large farms reduce their environmental impact while maintaining productivity.
What are the challenges of implementing sustainable farming?
Challenges include the initial cost of transitioning to sustainable practices, lack of access to resources and technology, and resistance to change. Education, policy support, and financial incentives can help overcome these barriers and promote the adoption of sustainable farming.
How can consumers support sustainable farming?
Consumers can support sustainable farming by purchasing products labeled as organic or sustainably sourced, supporting local farmers’ markets, and advocating for policies that promote sustainable agriculture. Being informed about food sources and choosing environmentally friendly options can drive demand for sustainable practices.