What is the Project?
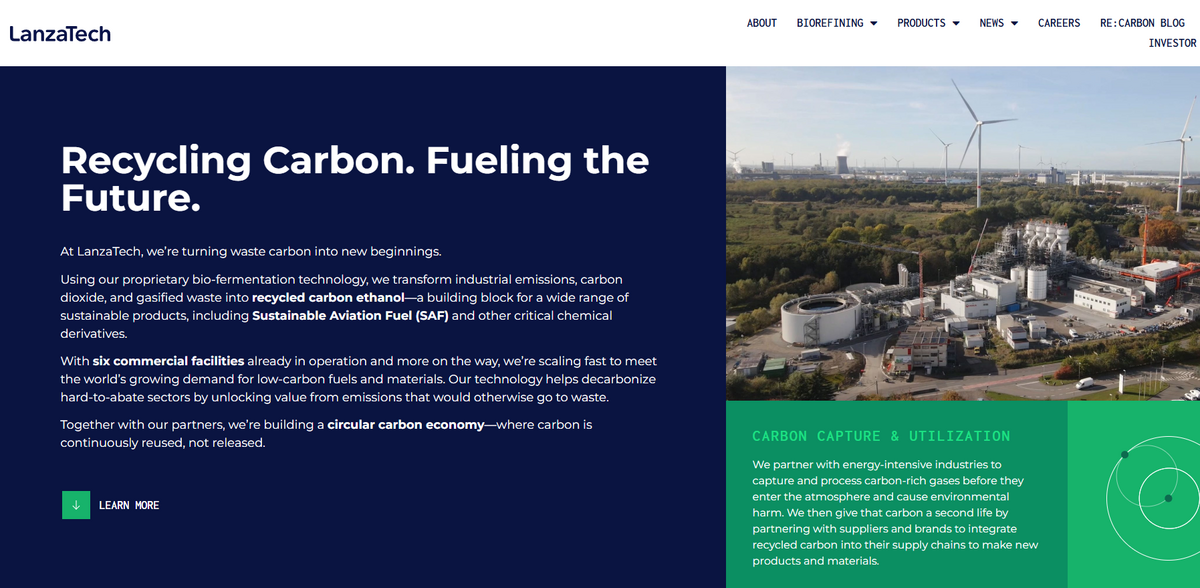
RECYCLING CARBON. FUELING THE FUTURE. LanzaTech is turning waste carbon into new beginnings. Using its proprietary bio-fermentation technology, the project transforms industrial emissions, carbon dioxide, and gasified waste into recycled carbon ethanol—a key building block for a wide range of sustainable products. This technology takes what was once seen as a liability and reimagines it as a resource. Imagine a future where recycled greenhouse gas emissions power airplanes, shampoo bottles have origins in steel mill emissions, and even used car tires find new lives as next year’s sofas… all made possible by this innovative approach.
Main Benefit of the Initiative
Key figures and facts:
- Six commercial facilities already in operation, with more on the way.
- Conversion of industrial emissions into recycled carbon ethanol.
- Production of Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF) and other critical chemical derivatives.
- Unlocking value from emissions that would otherwise go to waste through a circular carbon economy.
- Decarbonization of hard-to-abate sectors through proven, scalable technology.
Technology and Process
The process is nothing short of revolutionary. It is akin to retrofitting a brewery onto an emissions source like a steel mill or even a landfill site, but instead of using sugars and yeast to make beer, emissions are converted by bacteria into fuels and chemicals. This rethinking of carbon’s role is changing perceptions—above-ground carbon is treated as a valuable resource rather than disposable waste. The project creates opportunities to recycle a “liability” into something truly valuable and sustainable, demonstrating that innovation can lead to tangible environmental progress.
Environmental Impact Considerations
Life cycle analysis (LCA) plays an essential role in understanding the environmental benefits brought by LanzaTech’s technology. With in-house LCA expertise and collaborations with key institutions globally—such as The European Commission’s Joint Research Council (JRC), the Roundtable for Sustainable Biomaterials (RSB), and the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO)—the project uses detailed methodologies that vary by region. Third-party analyses, including studies published in Nature Biotechnology, help ensure transparency and accuracy. Emphasis on LCAs means that all energy and chemical inputs, along with transportation impacts, are carefully considered, demonstrating that every step is measured and optimized for environmental stewardship.
Innovation in Carbon Recycling
At its core, LanzaTech’s approach is driven by the idea that carbon recycling can reshape the way industries operate. It is a tangible example of transforming wasted emissions into valuable products. The technology is not static—it is continuously evolving as more facilities come online and collaborations deepen. As industries move toward decarbonization, this project becomes a catalyst for broader change. Emissions that once contributed to environmental harm are now given a second life, integrated into supply chains by partners and brands. The innovative spirit behind the process makes the technology a frontrunner in today’s push for a sustainable future… and it shows that passion for progress can turn an environmental challenge into an opportunity.
Project Impact on Sustainability
- SDG 7: Affordable and Clean Energy – by advancing renewable fuel and chemical production.
- SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure – through the development of cutting-edge bio-fermentation technologies.
- SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production – by promoting a circular carbon economy that continuously reuses carbon.
- SDG 13: Climate Action – by significantly reducing emissions from hard-to-abate sectors.
Future Perspectives and Global Collaboration
Looking ahead, the future of carbon recycling appears promising. LanzaTech’s technology envisions a world where pollution is no longer just emitted into the atmosphere but is captured, transformed, and reused as a critical resource. With six commercial facilities operational and new ones being planned, the project is scaling fast to meet the world’s growing demand for low-carbon fuels and materials. This initiative is a vivid demonstration of what can be achieved through global collaboration. Specialists from institutions like Argonne National Laboratory (ANL), Michigan Technological University (MTU), Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), and many others, continue to refine and validate the technology. As more research and peer-reviewed LCAs become available, the impact of transportation and other logistical elements on the overall sustainability footprint is steadily reduced. In essence, turning emissions into economic value not only supports industries but also marks a pivotal shift towards a future where waste carbon fuels both innovation and a cleaner environment.